Install
sh
$ npm add virtual-list-coresh
$ pnpm add virtual-list-coresh
$ yarn add virtual-list-coresh
$ bun add virtual-list-coreVirtual List Structure
virtual-list-core uses a virtual scroll mechanism, and when using it, you need to follow a specific layout structure.
Structure Image
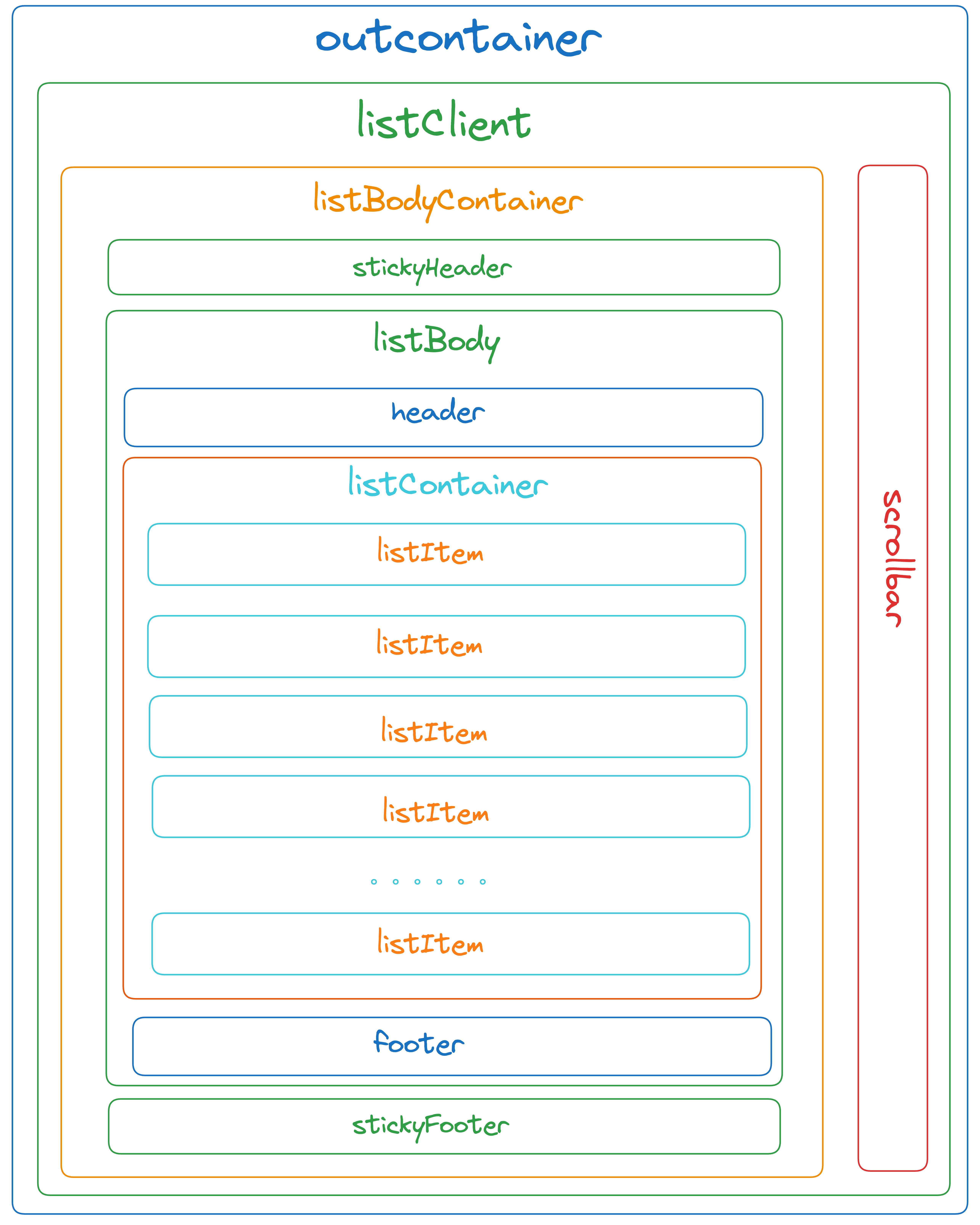
html
<div class="virtual-list__client">
<div class="list-body__container">
<div class="`virtual-list__sticky-header"></div>
<div class="virtual-list-body">
<div class="virtual-list-header"></div>
<div class="list-body__content"></div>
<div class="virtual-list-footer"></div>
</div>
<div class="virtual-list__sticky-footer"></div>
</div>
<div class="virtual-list-scrollbar"></div>
</div>Simple Usage
By passing in the corresponding configuration options, you can create a new virtual list class, and a virtual list instance will be returned. This instance provides access to the list’s state and corresponding methods API. You can obtain the range of elements that need to be rendered in the VirtualListEvent.UPDATE_RENDER_RANGE event, and then render the corresponding elements.
ts
import { BaseVirtualList } from 'virtual-list-core'
const virtualListIns = new BaseVirtualList(
{
clientEl,
bodyEl,
list,
itemKey,
// ......
},
{
[VirtualListEvent.UPDATE_RENDER_RANGE]: onRenderRangeUpdate,
[VirtualListEvent.UPDATE_VIRTUAL_SIZE]: onVirtualSizeUpdate,
[VirtualListEvent.UPDATE_VIEW_RANGE]: onViewRangeUpdate,
[VirtualListEvent.UPDATE_ITEM_SIZE]: onItemSizeUpdate,
[VirtualListEvent.UPDATE_TRANSFORM_DISTANCE]: onTransformDistanceUpdate,
[VirtualListEvent.SCROLL]: onScroll,
[VirtualListEvent.SCROLL_TO_TOP]: onScrollToTop,
[VirtualListEvent.SCROLL_TO_BOTTOM]: onScrollToBottom,
[VirtualListEvent.RENDER_LIST_CHANGE]: onRenderChange,
},
);
const onRenderChange = (
renderRange: { renderBegin: number; renderEnd: number },
renderList: T[],
) => {
renderNode(renderList, renderRange);
};